Angioplasty and Why is it Done?
What is Angioplasty?
Angioplasty, also called balloon angioplasty, is a procedure that opens arteries to let blood go through more easily. Healthcare providers use this minimally invasive procedure in tight spots in arteries where plaque makes the space inside an artery too narrow or blocks it.
When do you need Angioplasty?
The doctor suggests Angioplasty because of several reasons. Some benefits of performing Angioplasty are:
- It helps to reduce chest pain.
- It helps to fight breathing problems.
- Angioplasty also deals with other heart failure factors.
- Angioplasty lowers the rate of blood clotting.
- It reduces the rate of mortality and heart muscle damage
- It reduces fatigue and improves the quality of life
- It improves kidney function
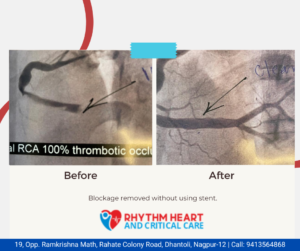
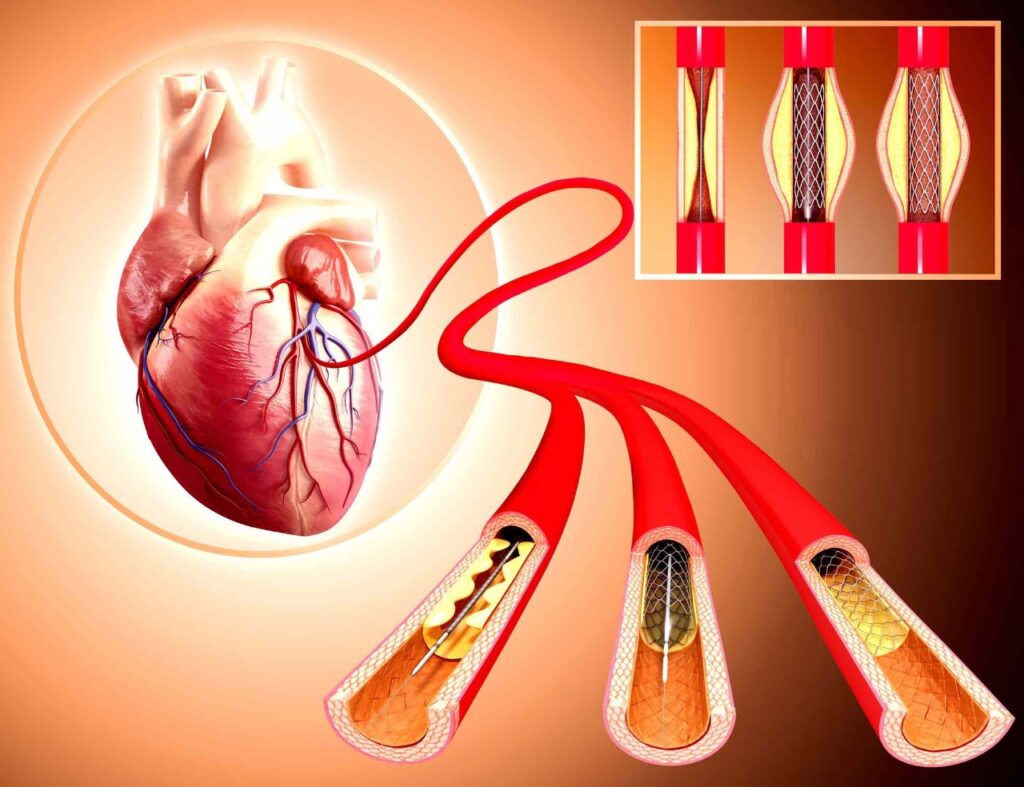
How is Angioplasty performed?
Explained by Dr. Pankaj Raut, Senior Consultant Cardiologist at Rhythm Heart and critical care Hospital, Nagpur, the procedure to perform angioplasty might seem easy, but it is not that simple. While performing angioplasty, doctors go through the following steps:
- The doctors insert a long, thin tube-like catheter in the crotch or wrist artery.
- The catheter is threaded into the affected artery using X-ray imaging.
- The surgeon then injects a liquid dye to check a blockage.
- Next, a catheter with a balloon is pushed through the first catheter and steered to the heart.
- The surgeon opens the balloon when the second catheter reaches its destination containing the blockage.
- After that, the balloon is removed along with the blockage.
- If required, the surgeon will then push another thin tube called the stent.
- This stent placement prevents the blockage’s re-growth and the narrowing of the artery.
- In the last stage, the catheter is successfully removed.
What are the risks or complications of Angioplasty?
It’s rare to have serious complications after an angioplasty, but every invasive procedure comes with occasional risks. For example, you may need an emergency coronary artery bypass graft during or soon after an angioplasty. Complications happen in around one in 100 procedures, although this might be higher or lower depending on your individual circumstances as discussed with Dr. Pankaj Raut.
Other Angioplasty risks include:
- A reaction to the dye.
- Heart attack.
- Abnormal heart rhythm.
- Stroke.
- Blood vessel or kidney damage.
- Blood clots.
- Chest pain.
- Bleeding.
- A repeat blockage if a stent isn’t placed in your artery.
The risk of angioplasty complications is higher for older adults or people who have several blocked arteries, kidney disease or heart failure.
How is Angioplasty beneficial after a Heart Attack?
The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions says that performing angioplasty is highly beneficial after having a heart attack. A Heart Attack can happen for several reasons, but the main reason is blood clotting in the arteries. Therefore, angioplasty helps rebound the blood flow in the heart and the body or organs quickly. If not treated, it can create severe damages to your heart muscles.