Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS) refers to the group of clinical syndromes which include along with acute myocardial ischemia (AMI), unstable angina (UA), ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction [NSTEMI). These group of clinical symptoms are high-risk manifestations of atherosclerosis and hyperlipidaemia, which leads to emergencies and requires urgent medical care and hospitalisation. A thorough clinical and physical assessment of the given patient’s history, physical findings, electrocardiography, radiological studies like 2D Echo and cardiac biomarker tests, helps clinicians to diagnose manage such cases. Patients often presents with chest pain which often radiates from chest to left arm, cardiac pain may be present from jaw till epigastrium.
Patients complaining with such clinical features often has dyspnea, anxiety, sweating, ghabrahat and nervousness. Thus, a 12 lead ECG can help the physician to diagnose the MI and differentiate it into STEMI and Which is later, confirmed with the elevated biological markers like Creatine phosphokinase-MB (CPK-MB), cardiac troponins like Troponin I and Troponin T, out of which, Troponin 1, is preferred for its sensitivity. Myoglobin levels can also be crosschecked during an early presentation of MI. Once a patient is diagnosed to have ACS, patient is required to be given Loading doses, which are Aspirin 300mg, Clopidogrel 300mg or Ticagrelor 180 mg or Prasugrel 60 mg along with Atorvastatin
80 mg, if patient is critical and needs to be referred, patient can be given Low molecular weight Heparin (LMWH). The patient should be referred to a hospital considering the window and golden hour of 60 minutes. If the Health care center has facilities of Thrombolysis but not PCI, center must consider the time period of 120 minutes, if patient can be shifted in that period to PCI center, shift the patient, and if cannot, thrombolysis or fibrinolytic therapy can be done, using alteplase, reteplase, and tenecteplase. If the patient presented
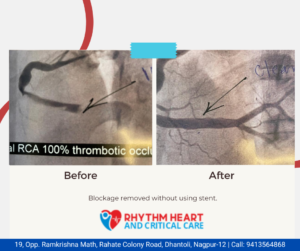
hemodynamically unstable, refer the patient to PGI center irrespective of the time durellon Patients diagnosed with NSTEMI has contraindication of Thrombolytic agents and requires only High-risk patients with UA and NSTEMI are often treated with percutaneous coronary intervent PCI) and aids in swift revascularisation of myocardium at risk of is chemia. Prognosis of the p optimised by revascularisation often followed by aggressive medical therapy, which includes anti- ischemic, antiplatelets, anticoagulants and statins. At the severe end of ACS spectrum is STEMI, I can be which usually has fibrin-rich thrombus which completely occludes epicardial coro cary artery. Patients with STEMI is required to undergo rapid reperfusion therapy, according to availability of the health care systems. Furthermore, STEMI can be managed with fibrinolytic therapy or PCI, where PGI is best. Patients, which are at high-risk, can be assisted with Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP). Besides stable and unstable angina, Prinz metal angina, which mimics the MI, needs to be managed with nitrates, as it is known to be caused due vasospasm of large coronary artery