- 19, Opp. Ramkrishna Math, Rahate Colony Road, Dhantoli, Nagpur -12, +91 9413564868
Coronary Angioplasty Indications
Coronary Angioplasty, also known as Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI), is a medical procedure used to treat blocked or narrowed coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart. When these arteries become clogged with fatty deposits (atherosclerosis), it can lead to chest pain (angina) or a heart attack. Coronary angioplasty helps to restore blood flow to the heart, significantly reducing the risk of severe heart complications.
Coronary Angioplasty in Nagpur
Coronary angioplasty is a life-saving procedure that plays a vital role in the treatment of coronary artery disease. By improving blood flow to the heart and relieving symptoms like chest pain, angioplasty can significantly improve the quality of life for patients with heart conditions. Though the procedure carries some risks, the benefits far outweigh the potential complications, especially when combined with a healthy lifestyle and regular follow-ups. With advancements in medical technology, coronary angioplasty continues to be a reliable and effective option for managing heart disease and preventing more severe heart-related events.
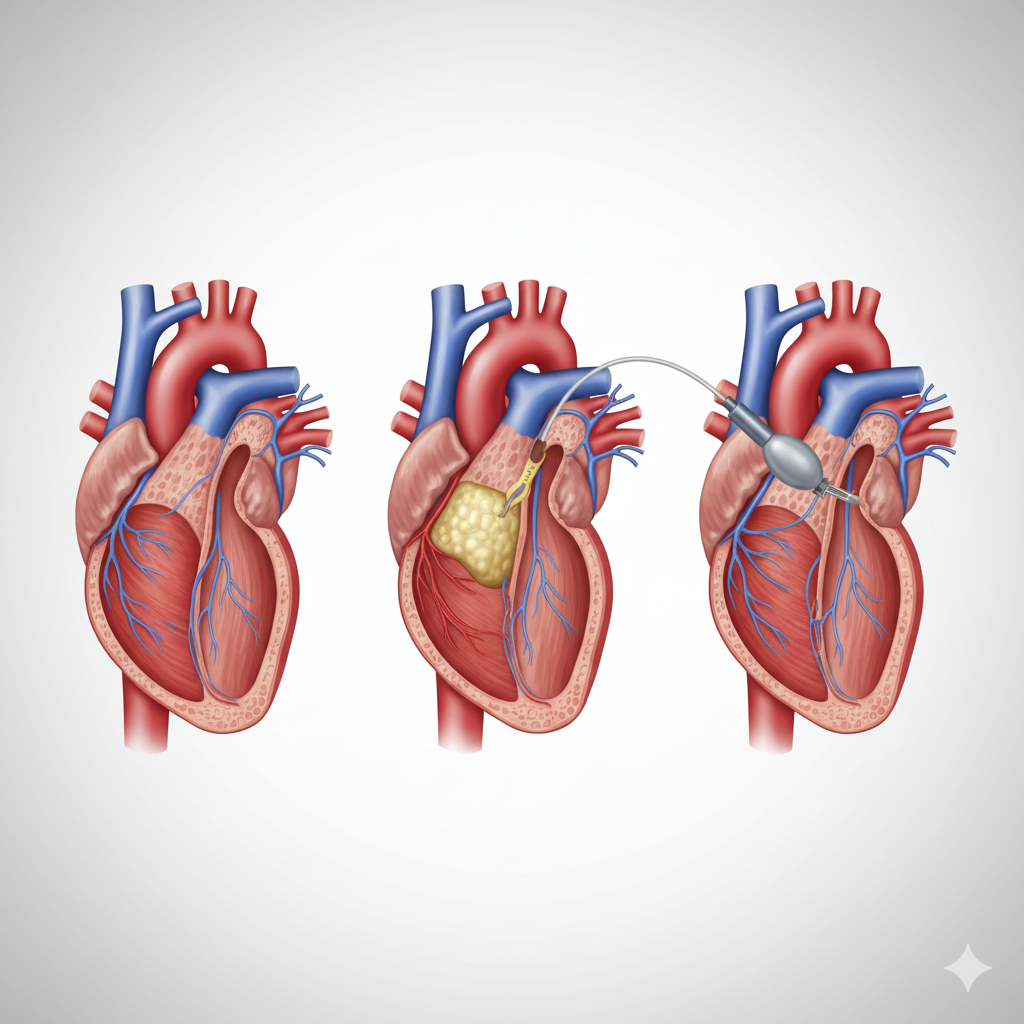
Benefits of Coronary Angioplasty
Coronary angioplasty offers several benefits, especially for patients with coronary artery disease (CAD):
Relief from Symptoms: One of the most significant benefits is the relief from chest pain and angina. By restoring normal blood flow to the heart, the procedure alleviates the discomfort caused by the blockage, helping patients return to their normal activities.
Reduced Risk of Heart Attack: Angioplasty lowers the risk of a heart attack by improving blood circulation. By removing or bypassing the blockage, the procedure reduces the likelihood of heart tissue damage due to inadequate oxygen supply.
Minimally Invasive: Compared to traditional open-heart surgery, angioplasty is minimally invasive. It doesn’t require large incisions, and the recovery time is typically faster, allowing patients to resume normal activities within a few days to a week.
Cost-Effective: As a non-surgical procedure, angioplasty is often more affordable than other heart surgeries, such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). It also requires a shorter hospital stay, which contributes to lower healthcare costs.
Recovery and Lifestyle Changes
After the procedure, patients are encouraged to adopt healthy lifestyle changes to prevent further heart issues:
Dietary Changes
A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins helps reduce the risk of further plaque buildup in the arteries.
Exercise
Regular physical activity, as recommended by a doctor, strengthens the heart and helps maintain a healthy weight.
Medication
Patients must adhere to prescribed medications, such as blood thinners, cholesterol-lowering drugs, and blood pressure medications, to keep their heart in good condition.
Avoiding Smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. Quitting smoking is essential for long-term heart health.
Regular Check-Ups
Follow-up visits to the cardiologist are important to monitor the patient’s progress and address any potential issues before they become serious.
Attend Regular Check-Ups
Regular follow-up visits with the cardiologist are essential to monitor the recovery process.

