- 19, Opp. Ramkrishna Math, Rahate Colony Road, Dhantoli, Nagpur -12, +91 9413564868
ECG Test for Heart
An Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a medical test that records the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time. It’s a simple, non-invasive test that provides critical information about the heart’s rhythm, electrical activity, and overall health. The ECG test is often used in hospitals, clinics, and even by healthcare providers in routine checkups. The results of an ECG can help diagnose various heart conditions and guide treatment decisions.
ECG in Nagpur
An ECG test involves placing small electrode patches on the skin of the chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes detect the electrical signals generated by the heart as it beats. The electrical impulses are recorded by the machine and displayed as a graph or wave on a screen or paper. This graph shows the timing of the heart’s electrical impulses and how they travel through the heart.
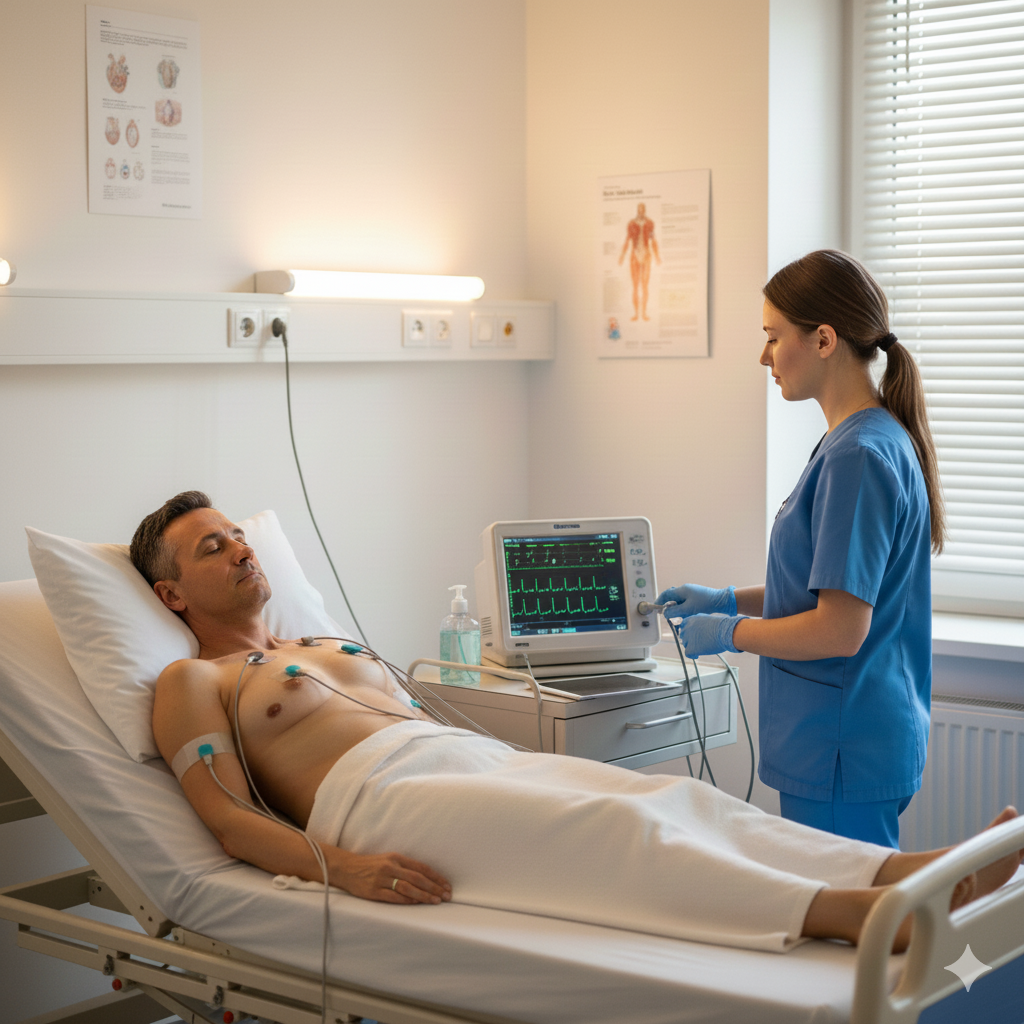
ECG Working Principle
During an ECG, the electrodes placed on the skin detect the electrical impulses that stimulate the heart. These impulses are recorded and displayed in the form of a waveform. The main components of the ECG waveform include:
P Wave: This represents the electrical impulse as it travels through the atria (upper chambers of the heart). The P wave shows the depolarization of the atria, which leads to the contraction of the atrial muscles.
QRS Complex: This represents the depolarization of the ventricles (lower chambers of the heart). It shows the electrical impulses traveling through the ventricles, which cause the heart’s main pumping action.
T Wave: This represents the repolarization (recovery) of the ventricles after they contract. It shows the electrical activity as the ventricles prepare for the next beat.
PR Interval: This is the period between the P wave and the QRS complex. It represents the time it takes for the electrical signal to travel from the atria to the ventricles.
QT Interval: This represents the time between the start of the QRS complex and the end of the T wave. It measures the time it takes for the ventricles to contract and then recover.
What to Expect During the Test?
Electrode Placement
Small adhesive electrodes are placed on your chest, arms, and legs to detect electrical signals from the heart.
Positioning
You will be asked to lie still on an examination table to ensure accurate readings.
Duration of the Test
The ECG procedure usually lasts about 5 to 10 minutes, making it a quick and efficient test.
Minimal Discomfort
The electrodes may feel slightly sticky or cool on the skin, but there is no pain involved in the test.
No Movement or Talking
To get clear results, it’s important to stay still and refrain from talking during the test.
Immediate Results
After the test, the electrodes are removed, and the heart’s electrical activity will be analyzed right away by a healthcare professional.

